

Since different isotopes of an element contain different numbers of neutrons in the nuclei of their atoms, isotopes of the same element will have different atomic masses. This is not the same as the element's mass. The sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called that element's mass number. Mass Number and Atomic Mass of Hydrogen, Deuterium, and Tritium Atoms They behave, chemically, like other hydrogen atoms.įigure 13.
Since atoms of both deuterium and tritium have only one proton in their nuclei, they only have one electron. An atom of deuterium has two particles in its nucleus, and tritium has three. Deuterium and tritium are isotopes of hydrogen. These are called deuterium or tritium, having masses of 2.014 amu and 3.016 amu respectively. There exist atoms of hydrogen that have either one or two neutrons in the nucleus in addition to the single proton. Each of these atoms has a mass of 1.008 amu. Most atoms of the element hydrogen contain only one proton in their nuclei. Isotopes can be most easily separated from each other using physical processes. However, the physical properties of the isotopes, such as their masses, bpoints, and freezing points, are different. This means it is difficult to separate isotopes from each other by chemical processes. All isotopes of one element have identical chemical properties. When an element has atoms that differ in the number of neutrons in the nuclei, these atoms are called different isotopes of the element. Diagram Comparing Hydrogen, Deuterium, and Tritium Atoms Since atoms are made of various numbers of these particles, it is unlikely that the mass of an atom other than carbon would add up to exactly a whole number.įigure 12. Even the masses of protons, neutrons, and electrons are ratios of their mass to carbon. The mass of an atom of another element is the ratio of its mass to the mass of a carbon atom. The mass of a 12C carbon atom is specified as exactly 12. The only exception is carbon, whose mass was used as a standard reference.

An amu is 1/12 the mass of one atom of 12C, or about 1.66 x 10-27 kg.Ītomic mass values for elements are almost never an integer.
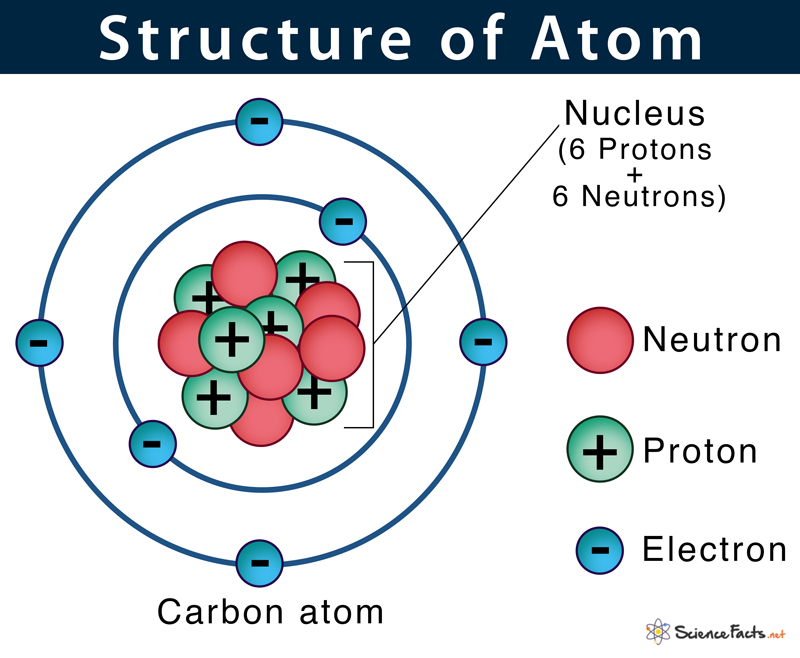
One atomic mass unit is a very small amount of mass. The mass of an atom or particle is expressed in atomic mass units or amus. To get an idea of how small an atom is, consider that a small gold coin may contain over 20,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 atoms. The smallest particle that would still have the properties associated with gold is an atom. How fine can the dust become and still be considered gold? The density of the cloud at any point is the probability of finding the electron at that point.įigure 10. The probability of finding the electron in any region of space can then be described by a cloud that rapidly thins out as one goes farther from the nucleus. We might think that the electron is rapidly moving around the nucleus and our experiment "catches" the electron as an instantaneous "snapshot" of it in motion. However, if we repeat this experiment many times, it will be found that the electron is much more likely to be located in certain regions of space surrounding the nucleus than in other regions of space. If we attempt to detect an electron in an atom, we might find evidence of it located almost anywhere around the nucleus. The electrons of the atom move rapidly around the nucleus. Because the protons are positively charged, the nucleus has a positive electric charge. In an atom, the protons and neutrons clump together in the center and are called the nucleus. If the proton and neutron were enlarged, and each had the approximate mass of a hippopotamus, the electron, enlarged to the same scale, would have less mass than an owl.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
